Asset Management
Asset and Fleet Management
When it comes to asset and fleet management, there are a lot of factors to consider, especially when it comes to large volumes of different types of assets. A company's bottom line can be greatly impacted by the efficiency and productivity of its asset fleet. That's why it's important to have a system in place that can help optimize fleet operations. There are many different ways to manage assets, and each has its own benefits and drawbacks.
So, what is asset management? In simple terms, asset management is similar to fleet management, but looks after all assets across the business from buildings to plant machinery and equipment tools.
In order to ensure that your machinery and tools are working as efficiently as possible, it is important to have a system in place for managing them. Not only will this help optimize production and save you money, but it will also increase safety on the shop floor. There are a number of different ways to manage your machines and tools, but the most important thing is to tailor the system to fit your specific needs. By taking the time to set up a machine and tool management system, you will be able to streamline your processes.
Why use software for the management of assets
In order to effectively manage a manufacturing, production or service providing process process, it is important to have an understanding of the machinery and tools used within the process. This includes not only knowing how to use the machinery and tools, but also how to maintain them, store them, and handle any potential safety concerns. Without proper management of the machinery and tools, the process can become inefficient and even dangerous. In this page, we will discuss some of the basics of machinery and tool management and provide some tips on how to best manage them.
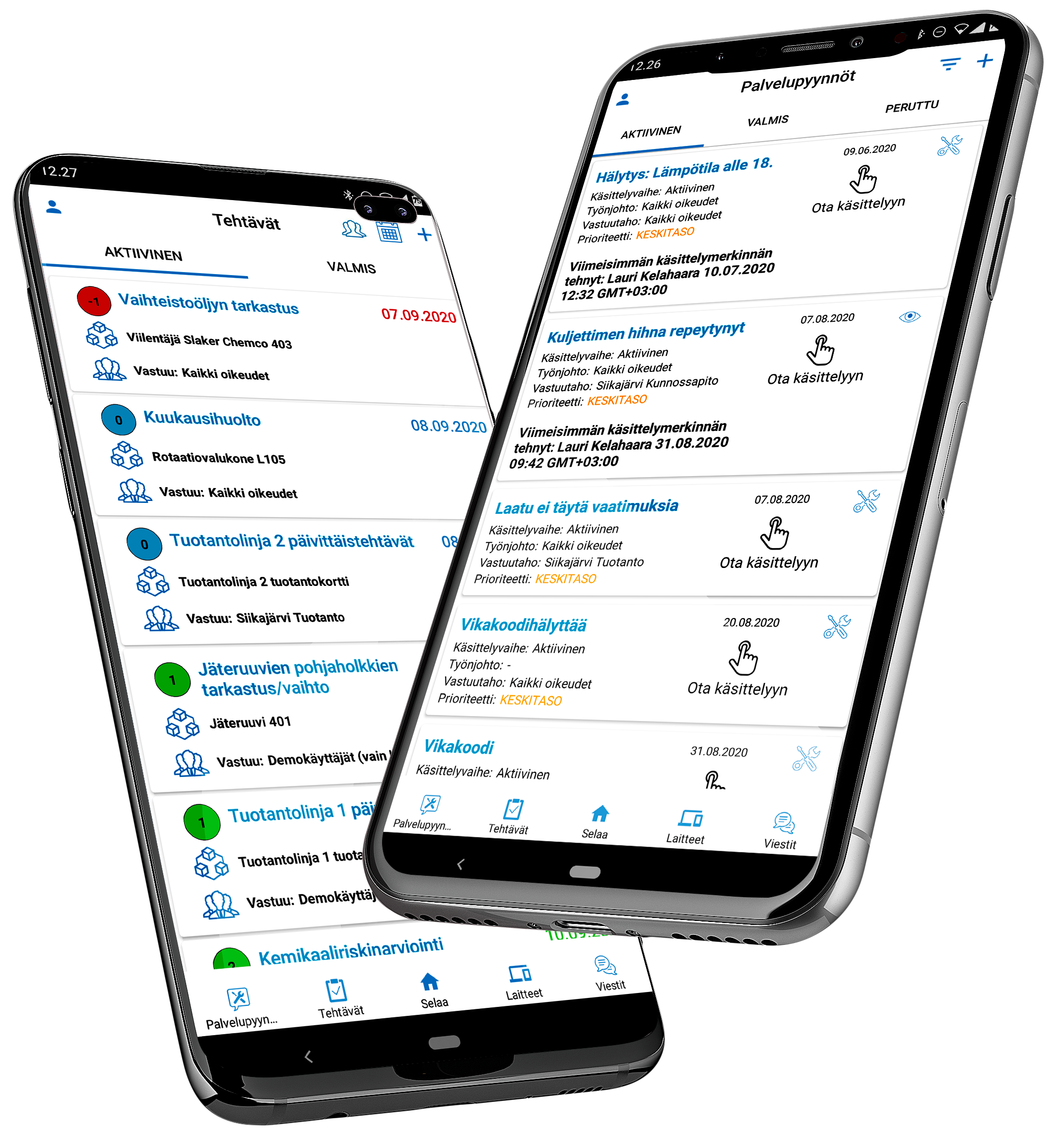
Machine and Asset management Software, is a class of software that helps manage the usage of tools, machines, and other resources. It can provide a number of functions such as inventory management, machine scheduling, upkeep and repair of machines (preventive and repairing maintenance). By reducing waste and improving utilization rates, the software can help save money for companies while also improving productivity. In recent years, there has been a significant uptick in the use of this type of software due to the increasing complexity and amount of different tools and assets used (like, for an example robots and drones)
As industries grow more complex, the need for sophisticated tools and processes grows as well. Drones and robots are two prime examples of this, as they are becoming more and more common in a variety of industries. Drones are being used more and more in fields such as construction, real estate, and agriculture. They offer an efficient and affordable way to get a bird's eye view of a job site or parcel of land. They can also be used to collect data and survey land. Robots are being used in a number of industries as well, such as manufacturing, health care, and food production.
As a business grows, the need for better and more efficient tools to manage and monitor the machines and tools used in production also increases. Spreadsheets were once the go-to tool for this, but they have several limitations. They are not good at managing large data sets, they are difficult to share and collaborate on, and they are not always up-to-date. A business could benefit greatly from replacing their spreadsheets with a software that is specifically designed for machine and tool management.
Kalustohävikki
Lost, broken and misplaced tools?
Asset management software can be a great way to keep track of your tools and machines. By inputting information about each asset into the software, you can create a database of all your assets. This will allow you to keep track of where each asset is, when it was last used, and what its current condition is. If you lose an asset, the software can help you to track it down. You can also use the software to generate reports on your assets, so that you can identify any patterns in tool or machine loss.
There are many reasons why tools, machines and other assets might go missing. Some of the most common reasons are listed below.
- The tool, machine or asset was not properly returned to its proper place or it was not properly secured
- It was not properly inventoried, it is unknown who last used it, where and when
- It was not properly tracked, there is no reliable information about its location
- It was not properly maintained, it broke down because its maintenance was neglected
What kind of problems does asset loss typically cause?
- Confusion and slowness into the process. As such, it is known that there should be equipment to use, but when it is searched, no working equipment can be found anywhere. In this case, the work cannot be carried out because the needed equipment is not in the right condition, when it is needed. Confusion, on the other hand, also leads to employee dissatisfaction, which in turn leads to other side effects.
- Financial losses. The company suffers financial losses when equipment is lost, it is acquired in vain (because it is not known what equipment would have been in use) and because the equipment breaks down. Furthermore, it is clear that part of the loss of equipment is due to theft, which is always easy to carry out when no one is in principle in need of equipment.
How to prevent loss of assets?
There are a few simple steps that can be taken to help prevent the loss of tools and other assets. The first is to create a system for tracking tools and other assets. This could include using a specific tool or software to track inventory, or assigning specific staff members to keep track of tools and other assets.
Another way to help prevent the loss of tools and other assets is to make sure that all staff members are aware of the importance of keeping track of them. This could be done through regular training, or by including information about asset tracking in staff manuals. Finally, it is important to have
Asset management Software
Mitä tehdään kalustonhallintaohjelmistolla?
Kalustonhallintaan tarkoitettu ohjelmisto pitää tyypillisesti sisällään seuraavia ominaisuuksia, joiden avulla yritys pystyy järkevästi toteuttamaan kalustonhallintaa (myös "EAM" eli "Enterprise Asset Management":
- Laiterekisteri, kohderekisteri ja kalustorekisteri
- Kaluston ostamiseen, hintaan ja nykyarvoon liittyvät tiedot
- Kaluston pysyvät tiedot (ns. "laitekortti")
- Kaluston ylläpitoon liittyvät tehtävä (ennakoiva- ja korjaava kunnossapito)
- Kaluston käyttöpäiväkirja
- Kaluston sijaintitiedot
- Kalustovaraukset
Kalustonhallintaohjelmiston tarkoitus on helpottaa kaikkea kalustoon liittyvää toimintaa - ei ainoastaan yrityksen johdossa vaan ennen kaikkea sen henkilöstön parissa joka laitteita työssään tarvitsee.
GPS Paikannus ja kaluston paikkatiedot
Mistä on kyse?
GPS-paikantamiseen perustuva kalustonhallinta perustuu aktiiviseen, oman virtalähteen, lähettimen ja datayhteyden sisältävän laitteen kiinnittämistä seurattavaan kalustoon. Tämä mahdollistaa reaaliaikaisen kaluston seurannan esimerkiksi karttapohjalle visualisoituna.
Kaluston GPS-paikannus on viime vuosina noussut vahvasti suuren yleistön tietoisuuteen (eikä vähiten tv-mainosten takia). Käytännössä liikkuvan kaluston GPS-paikantamista on tehty jo pitkään eri toimialoilla, erityisesti logistiikkaan ja kuljetukseen (rahti) sekä kunnossapitoon (lumiaura) tai palvelutuotantoon (esim. työkoneet) liittyen.
Käytännössä puhutaan laitteista, jotka tarjoavat virtaa itsenäisellä GPS-laitteelle tai esim. ajoneuvoista, joiden OBD- tai muuhun tietoliikenneporttiin voidaan suoraan kytkeä erillinen GPS-laite. Nykyisin myös laitevalmistajat valmistavat omaan kalustoonsa liittyen suoraan tehtaalla GPS-paikantamiseen soveltuvat ratkaisut.
Onko GPS-paikantamiseen perustuva kaluston seuranta aina perusteltua ja kustannustehokasta?
Oletuksena on tällöin, että jonkun henkilön työtehtävien kannalta on tärkeää saada tietää reaaliaikaisesti, missä laite liikkuu. Toisaalta voidaan myös ajatella, että jonkun on tärkeää tietää, mikäli kalusto liikkuu jollakin alueella. Kaluston on siten oltava suhteellisen toimintakriittistä ja arvokasta, että reaaliaikaisen kaluston paikantamisen voidaan katsoa olevan perusteltua.
Tyypillisesti reaaliaikaista kaluston paikantamista käytetään ajoneuvoissa ja isoissa työkoneissa, ei niinkään yksikköhinnaltaan esim. 100,00 € - 3000,00 € arvoisten työkoneiden ja laitteiden hallinnassa. Tähän on selvä syy: kustannustehokkuus häviää.
Itsenäiset ja omatoimiset GPS-laitteet muodostavat asiakkaalle kustannuksia seuraavasti:
- laitteen investointihinta TAI laitteen palveluvuokra
- laitteen tiedonsiirtoyhteys (voi kuulua palveluvuokraan)
- laitteen vikaantuminen/rikkoontuminen
- laitteen vikatilanteiden hoitaminen (esim. laitteen korvaaminen uudella)
Kuvan taulukossa on laskettu esimerkkikustannuksia aktiivisen GPS-paikantamisen ratkaisulle. Kuvasta voidaan päätellä, että isommilla kalustomäärillä kustannukset eivät liiku kymmenissä, vaan sadoissa tuhansissa euroissa.
Mikä on kustannus aktiiviselle GPS-paikantamiselle, jos kalustoa on satoja - tai tuhansia kappaleita? Voidaan helposti päätellä, että aktiivinen seuranta on mitä suurimmalla todennäköisyydellä liian kallis ratkaisu tähän tarkoitukseen. Toisaalta on myös muistettava, että laite, joka itsessään sisältää piirilevyn, mikroprosessorin, akuston ja virransyötön, on takuuvarma huoltokohde itsessän, mitä pidemmälle sen elinkaaressa liikutaan. Näin ollen sadat itsenäiset GPS-paikantimet tulevat vaatimaan myös jatkuvaa ylläpitoa ja huoltoa (korjaukset, buuttaukset, vaihtamiset).
Aktiivinen GPS-paikantaminen on varmasti perusteltua ja tarpeellista sekä kustannustehokasta sellaisessa kalustonhallinnassa ja silloin, kun:
- Kaluston tarkkaa sijaintia tarvitaan usein, reaaliaikaisesti tai tietokantaan "pisteinä" joiden perusteella dataa hyödynnetään muissa sovelluksissa
- Kalustoa on suhteellisen vähän (kymmenistä muutamaan sataan) ja se on homogeenistä
- GPS-Paikantimien asennusolosuhteet takaavat niille häiriöttömän toiminnan (= joku ei joudu jatkuvasti tekemään töitä niiden toiminnan osalta)
Aktiivinen GPS-paikantaminen ei todennäköisesti ole kustannustehokasta sellaisessa kalustonhallinnassa ja silloin, kun:
- Kalusto on tuhansista satoihin
- Kaluston sijainti tarvitaan vain ajoittain eikä sen "polkua" tarvitse seurata
- Kalusto on moninaista (esim. työkoneita, pienempiä sähkölaitteita, akkusähkötyökaluja, vuokralaitteita)
- Kalusto ei sisällä valmiita sähkönsyöttöjä/liitäntäportteja aktiivisille GPS-paikantimille vaan ne joutuvat toimimaan akkuvirralla ja niitä joudutaan lataamaan



